It has become a daily gesture, and even one of the most important ones. We wake up, we have a coffee, then we authenticate ourselves. Today, more than ever, we have a digital life and a duty to protect it. With Damien Leveque, CTO of Wemanity Secure, let’s talk about what digital authentication is and the good habits we should have…
1. Why Talk About Authentication?
Everyday users seek convenient solutions and often choose ease in managing their virtual identities. Because most people don’t realise the role they play in their own cybersecurity. According to Verizon’s 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report, 85% of breaches involve the human element and, to a certain extent, carelessness or a lack of knowledge on the subject.
“This trend is unfortunately not improving, so it is important to raise awareness. I want to talk about the techniques and tools that exist and that I use. So that everyone can find the protection method that suits them; to raise awareness to increase your own cybersecurity.”
Damien Leveque.
2. What is Authentication?
In the literal sense, authentication makes it possible to show that something is indeed the original.
Now, authentication is more about our digital identity. It is a method which by encryption and decryption protects the personal information of a user but guarantees that the user is indeed whom he claims and that he is authorised to access certain dematerialized resources.
“It allows you to secure access, to ‘open the doors’ to a personal space. At first, you only needed a username and password for one service. But the development of online activities means that authentication no longer protects only certain email accounts, but your life.” Damien Leveque.
3. What is the Difference Between Authentication and Authorization?
“In general, everything starts with an authentication process, we check your identity that you are known for , then comes the authorization, we check that you have received the right to access the desired resource. Authorization is therefore an additional privilege granted, for example, in companies where you have access to a space related to your tasks or to the tools you need but which are not specific to you. It is also your responsibility to protect access to these resources even if they are not yours.” Damien Leveque.
4. What is the Role of Authentication?
Authentication therefore allows organisations or individuals to secure their networks by allowing only authenticated users or processes to access their protected resources.
“Authentication is everywhere, it concerns computer systems, networks, databases, API, Websites and other applications or services that operate over the internet or through a network.” Damien Leveque.
5. What are the Main Types of Authentication Factors?
Several authentication factors generally go through a key or information that we know (like a password), that we have physically (like a card), and biometric (like a fingerprint).
The most common authentication methods are…
Password authentication
Password authentication provides a simple method to establish if an identity is authenticated by using a defined editorial or numeric key.
“Today, software used by hackers makes it possible to test all the words in a dictionary or all possible combinations of characters. With the increase in the power of computers, this process is faster and faster, hence the importance of defining ever longer and more complex passwords.” Damien Leveque.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is a security process that relies on the unique biological (physical or behavioural) characteristics of the user. We mainly find this type of authentication on our phones to unlock them. It allows you to authenticate yourself in a simple and secure way without having to memorise a combination.
“However, you should be vigilant. To avoid storing and securing your biometric data, popular services that offer this authentication factor only offer a shortcut to a user/password combination.” Damien Leveque.
The Authentication Token
A token or authentication token is an electronic key transmitted to a user to access a restricted resource. This trust device allows you to provide an additional factor to confirm your identity. It provides a second layer of security and administrators have detailed control over every action and transaction.
“I am often asked which are the most effective factors. In reality, it is not a type or technology of factors that protects, but their number. Some hackers use social engineering by using their victims’ personal information to guess the passwords of the services they use. So even our most intimate codes are not immune. […]
The more verification checks you define, the more certain you are that the information is unique and that the person logging in is the right one. This is why double or even triple authentication is very effective, because it greatly complicates the task of hackers.” Damien Leveque.
6. What is Two-Factor Authentication?
“When we talk about two-factor authentication, we are adding a step. […] Today, we believe that we need an additional factor to confirm an identity reliably.
A very common example is when you enter your username and password and then a service, offering a high degree of security, asks you for a temporary code (OTP), often in the form of a 6 or 8 digit key. The most common way to receive it being by SMS or email, but I do not recommend it, because it is quite easy for a hacker to manage to intercept it (SIM-swapping). Prefer the use of an application on your phone such as Google Authenticator (available on Android or Apple) or better, an application locked by a cryptographic key like Yubico Authenticator (Android or Apple). The advantage is that if an attacker gets their hands on the first factor, they will never be able to complete the authentication without the second factor and therefore your approval.” Damien Leveque.
The OTP (One Time Password) is an automatically generated string of characters that authenticates a user for a single transaction or connection. Indeed, this code generally expires after a few seconds, leaving very little time for a malicious person to intercept it and steal your identity.
Sometimes sites or applications offer you to configure this security, but it is advisable to always check your account settings to ensure that this option is available.
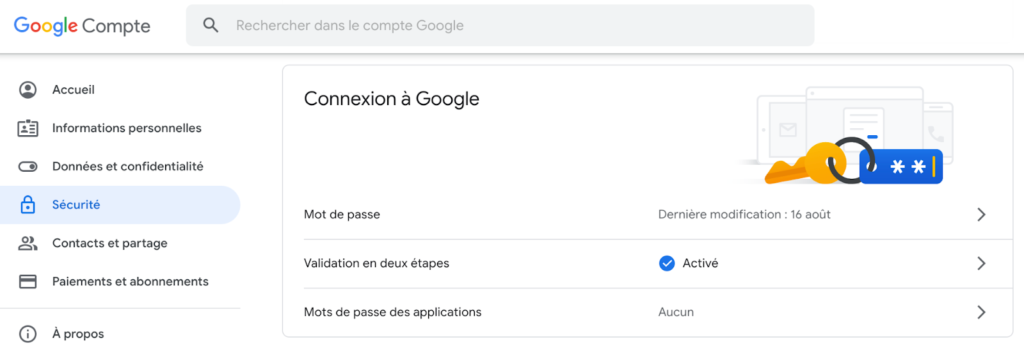
Source : Google account of Damien Leveque
7. How to Set the Best Password?
First, you need to define a password that is complex enough not to be guessed.
“Two criteria can help you: the length of the password and its ultra-personal aspect. […] We too often forget that we can put spaces, accents… A sentence, for example, is a good way to complicate and memorise a code. Add some capitals to this sentence and replace letters with numbers or logical symbols. Like a ’1’ or ’!’ for a lowercase ’L’ or ’$’ for an ’S’. With this, you will get a password that is more resistant to hacking and easier to remember.[…]
If you have a lot of accounts and are worried about your memory failing you, use digital safes, software like KeePass or Bitwarden, which I recommend using instead of your internet browser (Chrome, Safari…), or your Post-its.
This software can provide you with other services such as generating random passwords or verifying that a password has been compromised in a hacked database.” Damien Leveque.
Secondly, this password must be unique for each site.
“A recurring mistake that makes life easier for hackers is to use the same password everywhere. Not all websites and applications have the same level of security. Hacking one of them could be disastrous, as it would expose all of your personal data. A hacker is well aware of this weakness and could test access discovered on different sites or applications that you use to extend the hack of a simple video game to your administrative spaces.” Damien Leveque.
Finally, they must be regularly updated.
“Sometimes our authentication data is exposed without our knowledge. Haveibeenpwned that I use and that is known to be reliable is very interesting because it consults hacked databases and tells you if your email address or password is there. […] Another practice that I recommend in order to limit the impact of a possible hack is to use 3–4 email addresses depending on the type of platform on which you are looking to register (Social networks, Newsletters, Accounts administrative…).” Damien Leveque.
8. What are the Limits of Authentication in Terms of Cybersecurity?
For the best authentication it is crucial to:
- Set complex and unique passwords,
- Systematically ensure the possibility of adding additional factors,
- Store in encrypted and secure spaces (or in your memory),
- Make sure you never share them.
“Even with someone who introduces themselves as tech support, a line manager, or email. Above all, never click on links in a hurry, because even if you do not provide any personal information, you become a victim of ever better-crafted scams.” Damien Leveque.
The limit of authentication is caution. As Damien Leveque explains, protecting yourself from authentication processes is neither complicated nor time consuming, but requires good habits.
“It can even become a game between all the customizable characters and mnemonics. It is up to everyone to adapt their method to secure their access. Be aware that we are vulnerable to hackers in the face of their ever more innovative techniques. Our best defence is vigilance.” Damien Leveque.
In summary:
It is a method that guarantees that the user is who he claims and that he is authorised to access certain dematerialized resources.
There are several authentication factors which generally go through a key or information that we know (like a password), that we have physically (like a card), biometric (like a fingerprint) and that can be produced (like a gesture).
Two-factor authentication (2FA) works by adding an extra factor of security to your online accounts. Obtaining this second identifier requires access to something that belongs to you.
The best password is long, memorable only by you, and varies in punctuation like a sentence. It is also a password that is not timeless.